An information security audit is systematically checking out an organization’s policies, processes, and systems for its ability to protect the data. The following sections of this blog will try to establish why information security audits are important and how they have benefits in any approach when making an organization stronger towards security.
What is an Information Security Audit?
An information security (IS) audit is essentially a deep inspection of all security practices of an organization, the technology of a company being used as well as the policies accompanying it. The primary objective of such an audit would be
- Data Security: Data breaches occur far more often than is common knowledge, and the audit ensures that your organization has enough safeguards in place to protect sensitive data.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements: Most industries require you to comply with rigid standards of data protection. Audits help you ensure you are adhering to these requirements to minimize the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: Audits, through the identification of vulnerabilities and analysis of risk, enable organizations to proactively fill security gaps.
- Building Stakeholder Trust: Customers, partners, and regulators all want to work with companies they can trust. A commitment to regular security audits signals a strong stance on data protection.
Key Phases of an Information Security Audit
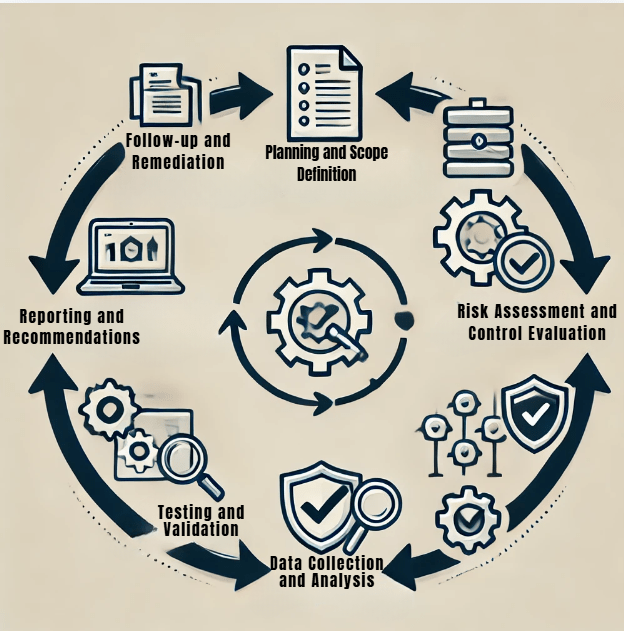
- Planning and Scope Definition: This is the step where the scope of the audit is defined: which systems, applications, and processes are to be reviewed. Organizations can also determine which standards to follow, for example, NIST or ISO 27001.
- Risk Assessment and Control Evaluation: A risk assessment determines areas that require intense scrutiny. In this stage, auditors check the technical and administrative controls- firewalls to password policies-and see how well they defend the data.
- Data Collection and Analysis: This is the phase where the audit evidence is gathered and analyzed. It may involve documentation reviews, system configuration analysis, and log file examination to confirm whether a system is resilient enough to ward off threats.
- Testing and Validation: Auditors test security controls by applying penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and configuration assessment. This will validate the effectiveness of current security measures.
- Reporting and Recommendations: Auditors summarize findings in a report structured to reflect identified risks, compliance gaps, and potential vulnerabilities. This report is accompanied by actionable recommendations to strengthen the organization’s security posture.
- Follow-up and Remediation: The organizations undertake remedial measures to the problems identified by the audit through corrective actions and security enhancements.
Common Areas of Emphasis in an Information Security Audit
An information security audit is a comprehensive review typically encompassing the following:
- Access Control: It makes sure that the right permissions are granted to users and nobody unauthorized accesses the data.
- Data Security: Verification of encryption and backup of data and prevents data loss, hence data is sure to be secured.
- Network Security: This involves verification of the firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and virtual private networks in the entire network internal and external threats.
- Incident Response Plan: The organization is certain to have an incident response plan for identifying, responding to, and recovering from an actual or suspected security incident.
- Physical Security: Covers physical controls, which comprise facility security, and ensures no unauthorized access to confidential information.
- Vendor and Third-Party Risk Management: Looks at the vendor’s security requirements to determine whether they align with the organization’s standard for security.
Important Benefits of Information Security Audit
- Improved Security Position: Regular audits of security vulnerabilities give an organization a chance to improve and change in response to emerging vulnerabilities.
- Compliance: Most regulatory bodies require auditing to ensure that data is handled responsibly. Companies will avoid penalties and reputational damage through the audits.
- Risk Management: Audits point out vulnerabilities, which allows organizations to focus on their high-risk areas and, therefore, strengthen their defenses.
- Increased Transparency: Audits ensure that stakeholders have clear insights into an organization’s security measures, hence building confidence and transparency.
Standards and Frameworks that Guide Information Security Audits
Organizations performing information security audits commonly rely on known frameworks in order to help them draw their conclusions:
- ISO/IEC 27001: The standard defines a framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an ISMS.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST framework is widely implemented across industries in order to help organizations manage and reduce their cybersecurity risks. To know more about it check this
- SOC 2: This applies to organizations that process sensitive customer data. In SOC 2, an organization’s ability to guarantee the security, availability, confidentiality, and privacy of its data are emphasized.
- COBIT: This gives framework support to IT governance and management practices, including security controls and audit practices.
Challenges in IS Audits
- Keeps pace with constantly changing threat.
- Resource intensive and usually require time, professional/technological skills, as well as technology.
- At times, enhancements made by the audit may impact to system usability. It must thus be planned and prioritized accordingly.
Conclusion
Information security audits are the backbone of a security policy, developing a defensive infrastructure and fostering security awareness across all organizational levels. As more sophisticated and challenging threats emerge, continuous scanning has become essential for organizations committed to protecting sensitive data, maintaining stakeholder trust, and staying ahead in an ever-evolving landscape. Digi9 offers comprehensive Information Security Audits, ensuring robust protection and compliance for modern businesses.


