Identify:
- Know your tools: Make a list of every device, software, and type of data your business uses. This includes computers, phones, tablets, cloud storage, and any other digital assets.
- Understand your data: Identify what sensitive information you handle, such as customer data, financial records, or intellectual property.
Create:
- Write a cybersecurity policy: This is like a rulebook for how your business should handle data. It should cover everything from passwords to how to report suspicious activity.
- Assign roles: Decide who is responsible for different parts of cybersecurity, like IT staff, managers, and even vendors.
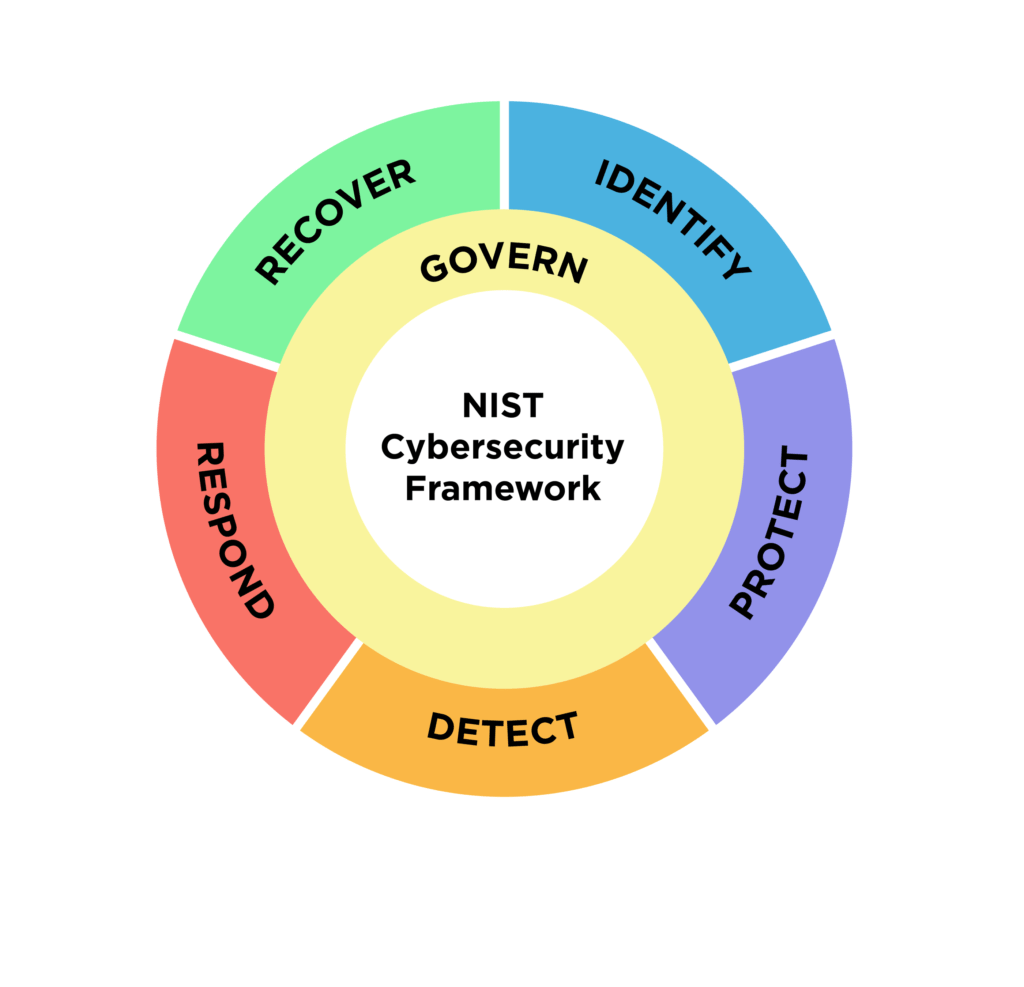
Protect:
- Lock it down: Control who can access your network and devices. Use strong passwords and limit access to sensitive information.
- Use security software: Install antivirus, firewall, and other tools to protect your systems from threats.
- Encrypt data: Scramble your sensitive data so that even if it’s stolen, it’s useless to hackers.
- Back it up: Regularly back up your data to a separate location, like an external hard drive or cloud storage.
- Stay updated: Keep your software and operating systems up-to-date to fix security vulnerabilities.
- Shred it: Have a policy for securely disposing of sensitive documents and electronic data.
- Train your team: Educate your employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices.
Detect:
- Keep an eye on things: Monitor your systems for unusual activity, like unauthorized logins or strange network traffic.
- Regular check-ups: Scan your network for vulnerabilities and signs of intrusion.
Respond:
- Have a plan: Create a response plan for what to do if your business is attacked. This should include how to notify customers and employees, and steps to contain the damage.
- Keep things running: If possible, keep your business operations going during and after an attack.
- Report and investigate: Notify the authorities and conduct a thorough investigation to understand how the attack happened.
- Learn from it: Use the incident to improve your cybersecurity measures and prevent future attacks.
- Prepare for emergencies: Have a plan for how to protect your data in case of natural disasters or other emergencies.
Recover:
- Rebuild: After an attack, fix your systems and restore your network to normal.
- Keep everyone informed: Communicate with your employees and customers about the recovery process.
By following these steps, you can significantly improve your business’s cybersecurity and protect your valuable data.


