As the adoption of cloud computing becomes faster, organizations holding sensitive data in the cloud require effective cloud forensics. Cloud forensics is simply a subset of digital forensic practice that focuses on investigating incidents, data breaches, and malicious activities carried out within cloud environments. Since cloud ecosystems are similar to complex patterns with data distributed across multiple servers and regions, it presents both challenges and opportunities for forensic investigators.
Importance of Cloud Forensics
With the design and development of cloud computing, the organization’s dependence on the cloud service provider for data storage and computing goes hand in hand. This fundamentally puts a critical need for cloud forensic capabilities within organizations to:
- Investigation of Data Breaches: A deep understanding of the type of breach, identification of compromised systems, and appropriate determination of the impact on the organization is a must.
- Maintain Authenticity: Cloud computing creates an environment that complicates traditional forensic procedures; an exceptional technique has to be adopted to maintain the purity and integrity of the digital evidence without any deviation.
- Compliance: Healthcare and finance are industries that are the most strenuous for compliance. Cloud forensics ensure that there exists forensic investigations while maintaining their compliance standards under a legal and industry perspective.
Key Stages of Cloud Forensics
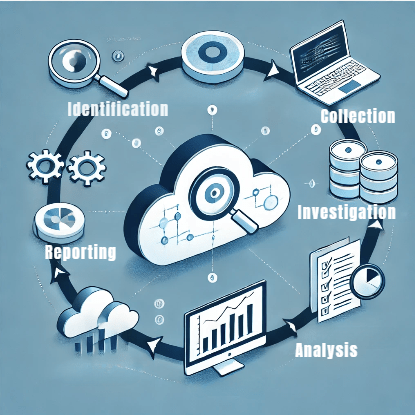
- Identification: The identification explains where exactly the security breach occurred. When investigating within the cloud, it identifies whether it happened at the infrastructure level, the platform level, or the application level.
- Collection: While cloud data collection is quite different from on-premise data collection, the way of traditional forensics differs. Forensic Investigators usually rely on the CSP to retrieve access logs, network traffic and the data stored. The tools of collection of evidence include AWS CloudTrail, Microsoft Azure Monitor and Google Cloud’s Operations Suite among others.
- Investigation: Once the data is gathered, it is then analyzed for anomalous behavior. The investigators look for any anomalies such as unauthorized logins, data exfiltration, or strange system behavior.
- Analysis: In the analysis phase, the evidence is correlated against the timeline of the attack to identify how the attack unfolded and in what extent the data was compromised.
- Reporting: All findings, methods used during the investigation and all recommendations for improving cloud security are provided in a detailed report.
Tools and Techniques
Cloud forensics requires specialized tools designed specifically for cloud environments. Some of the common tools include the following:
- AWS CloudTrail: This tool tracks the user activity and API calls. This is an extremely valuable audit trail for forensic investigations.
- Google Cloud Operations Suite: It offers full logging, monitoring, and tracing services, which helps investigators to obtain the necessary evidence.
- Azure Security Center: A tool for security offered by Microsoft, facilitating detection of threats, security analytics, and investigation in cloud environments.
- Other tools used in cloud implementation include FTK Imager and EnCase. However, to access the cloud systems, one would have to seek assistance from the concerned CSPs. To know more about these tools ,click here
Cloud Forensics Challenges
While cloud forensics presents several advantages, there are several major challenges that will be elaborated as follows:
- Data Accessibility: The evidence in cloud environments is hard to reach due to multi-tenancy. To store the customer data on shared infrastructure makes the legalities involved in accessing evidence difficult.
- Jurisdictional Issues: Cloud data is very likely spread over different geographically located places where locally relevant laws may apply. It is very hard to identify the laws of a single jurisdiction which would apply in such a distributed environment to the forensic investigation.
- Ephemeral Data: The data in the cloud is transient, and much of it fails to capture information in a sufficient time frame before being overwritten or deleted. The forensic investigator therefore has to react on a very short time scale.
Conclusion
Cloud forensics has been an increasingly important part of cybersecurity and a concerned area with the increasing adoption of cloud services by organizations. Due to technical tools to overcome challenges in dealing with data accessibility and jurisdiction, forensic investigators can help organizations unearth the truth behind security incidents and safeguard sensitive information in the cloud.


