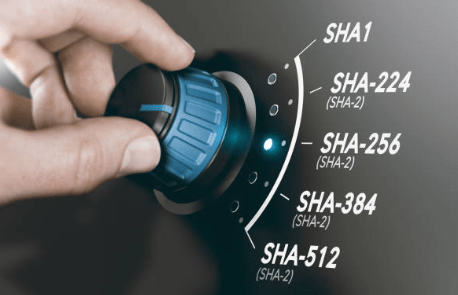
Hashing is one of the best methods to provide data integrity and authenticate the digital evidence in the domain of digital forensics. Algorithms for hashing create digital “fingerprints” on files to detect even minimal changes made to data. This blog will explore the concept of digital hashing, its utilization in digital forensics, types of available hashing algorithms, and best practices for data integrity using hashing. What is Digital Hashing? Digital hashing is the process of taking a piece of data—such as a file, text, or an entire disk image—and changing it into a fixed-size string of characters, represented typically as a hexadecimal number. This unique “hash” is a digital fingerprint of the original data. The hashing process is deterministic, meaning that, given the same input data, the same hash will always be produced, while the smallest change in the data will produce a hash quite different from the original. Hashes in digital forensics ensure that evidence collected up to a point of presentation in a court of law has not been tampered with. Hash values can be recomputed through different stages to ensure nothing has been tampered with. Why Digital Hashing Matters in Forensics? Digital hashing, therefore, is important to digital forensics for some very important reasons: Hashes are a way to prove that evidence has not been tampered with. For example, in the collection of digital file, forensic experts generate its hash. During analysis or transmission of such evidence, the hash is generated again and compared to the hash during the time of collection. If it’s the same, then the data hasn’t been changed. Hashing ensures that investigators show evidence to have been held securely from the time of reception into custody. In generating and recording hash values, each stage of the forensic process can be shown for which evidence has been kept under control, thus showing lower chances of a court case. To know more about chain of custody, check this This allows for fast and effective comparison of large data sets. Rather than comparing every byte of two files, investigators can just check if their hash values match or if changes have been made. Another significant use of hashes is that of validating digital signatures, which verify the sources of data. Hash values are frequently used in malware analysis to identify known malicious files by comparing them with existing databases of malware hashes. Types of Hashing Algorithms Different hashing algorithms exist, with varying levels of security and uses. Some of the most common hashing algorithms used in digital forensics are listed below: How Hashing is Used in Digital Forensics Hashing algorithms are mighty tools used in digital forensic investigations in many ways: Key Tools for Hashing in Digital Forensics 1. Kali Linux Kali Linux, a popular Linux distribution for digital forensics, comes pre-loaded with tools like sha256sum, md5sum, and other command-line utilities that allow quick and efficient hashing. Forensics professionals use these tools to verify the integrity of evidence files and confirm that files haven’t been altered during acquisition and analysis. Usage: Advantages: Kali Linux provides a straightforward way to hash files with reliable algorithms, making it an essential tool for forensic verification. 2. OpenSSL OpenSSL is a powerful cryptographic toolkit available on most Linux distributions. It supports various hashing algorithms and is often used for command-line hashing on Kali and other Linux systems. Usage: Advantages: OpenSSL’s versatility in hash type selection makes it ideal for verifying data integrity across formats. 3. HashMyFiles A lightweight Windows-based tool, HashMyFiles supports bulk file hashing, allowing investigators to quickly generate and compare hash values for multiple files. Best Practices for Using Hashing in Digital Forensics Effective hashing follows a few best practices: Limitations of Hashing Hashing is a very fundamental component of digital forensics, yet not without its limitations. First, Conclusion Hashing is one of the vital components of digital forensic analysis. It provides individuals with a reliable and ensured means of maintaining integrity within digital evidence. This helps in preserving the evidence as it is acquired up to the time of presentation with the help of algorithms like MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-2. In addition, best practices in investigators ensure that hash values are recorded for evidence files and updating their databases of malware hashes also reinforces the data integrity. Despite the limitations, hashing remains one of the best methods applied in digital forensics since it is helping experts to attain justice through the preservation of digital evidence integrity.