In modern digital life, email forensics is an essential line of defense against the misuse of email for phishing, fraud, malware distribution, and unauthorized data transfers. While emails are the primary communication channel in both personal and professional sectors, they are also exploited by attackers with ill intent. Email forensics, a branch of digital forensics, plays a crucial role in tracing evidence of these malicious activities, identifying potential threats, and enhancing cybersecurity. This specialized area is designed to gather evidence, uncover illicit actions, and strengthen defenses against email-based attacks.
This article will cover the fundamentals of email forensics, including the tools and techniques employed, the investigative process, and the unique challenges facing forensic experts in today’s evolving cyber landscape.
What is Email Forensics?
It involves tracing the origin of an email, examining its metadata, identification of malicious attachments and links, and understanding communication patterns involved. Through this type of forensics, an investigator can trace down where the attack came from, uncover evidence for fraud or harassment, and gather actionable insights into tightening security.
Cyber importance of email forensics can be traced to multiple factors:
- Prevention of phishing and spoofing attacks: it can outline, from fraudulent emails’ point of view, how phishers or spoofers impersonate a legitimate institution and education of users with relation to identifying phishing.
- Reduction of data breach: Emails normally contain confidential information of people. Forensics email may expose the intent as well as accidental leaked of secret data.
- Incriminating evidence: In cases of fraud or harassment can be provided through email forensics. Their criminal activities get well-timed evidence during the court process.
- Malware Detection: Most malware begins with an email. As emails forensics helps in describing the malware attached, stopping its spread of attack.
Key Steps in the Email Forensics Process
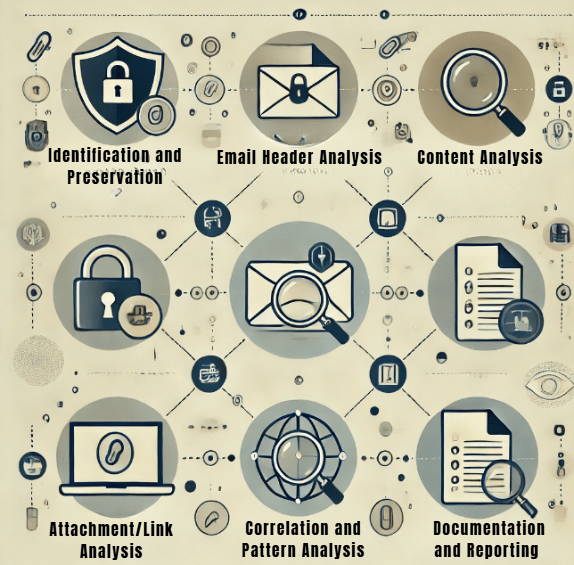
- Identification and Preservation:
- Identify relevant email accounts, messages, or servers that need examination.
- This data is then preserved to maintain its integrity. Investigators create an exact copy (or image) of the email data to analyze without altering the original evidence.
- Email Header Analysis:
- All metadata in an email’s header, which includes information such as the sender’s IP address, mail servers used in transit, time stamps and route taken by the e-mail.
- One finds out the origin of the mail and checks whether the mail is tampered with or spoofed by analyzing the headers.
- Content Analysis:
- Examines the content of an e-mail, which includes body text and attachments.
- Investigators scan for any suspicious keywords, phrases, and attachments that may indicate something malicious is going on.
- Attachment/Link Analysis:
- Email attachments and links are more commonly used for phishing purposes, spreading malware, or unauthorized data exfiltration. Forensic experts will employ specialized tools to check a link or file for a malicious code or an unauthorized connection.
- Correlation and Pattern Analysis:
- Email forensics usually involves the analysis of a chain of emails or pattern of communication.
Analysis process helps identify the patterns repeated, correlate with other evidence forms, and the scope of the attack.
- Email forensics usually involves the analysis of a chain of emails or pattern of communication.
- Documentation and Reporting:
- All the findings are documented in an extended report that indicates evidence, analytical processes, and conclusions.
Reports must be truthful, informative, and legally valid to be taken as evidence in court when required.
- All the findings are documented in an extended report that indicates evidence, analytical processes, and conclusions.
Email Forensics Tools
Effective investigations are possible through the use of several tools and techniques by email forensic examiners:
- Forensic Email Collector (FEC): A tool for grabbing email evidence from multiple Web-based services, including Gmail, Yahoo, and Office 365.
- MailXaminer: A specific tool that has multi-format email examination capability and allows keyword searching, link analysis, and detailed email header examinations.
- FTK (Forensic Toolkit): Powerful search, visual, and data processing functions on emails and attachments
- Xplico: An open-source software tool that helps in getting email headers and content based on network packets; that can be used when investigation is done on the bases of intercepted emails.
- Email Header Analyzers: Websites such as MxToolbox and IP Tracker help trace IP addresses and analyze email headers to validate the legitimacy of senders.
Email Forensics Challenges
Email forensics is a challenging field with its own set of challenges:
- Encryption and Privacy Controls: More and more encryption and privacy controls are making it difficult to access emails legally and ethically.
- Volume of Data and Intricacy: In a company, the volume of email may be huge sometimes, and searching for one piece of evidence related to an investigation may be such a daunting task.
- Spoofing and Obfuscation : Cybercriminals use spoofing techniques to mislead the recipient of the message using incorrect addresses that make it even more challenging to trace who the true sender is.
- Cross-Border Legal Issues: Evidence based on email normally crosses borders, giving rise to jurisdictional concerns and problems with data protection compliance.
- Emerging Threat Environment: Attackers are changing, including new types of phishing attacks and malware that traditional forensic tools fail to detect.
Email Forensics Best Practices
Best practices should be followed by forensic investigators to conduct a successful investigation:
- Collection and Acquisition in a Controlled Manner: Email data must always be collected, imaged, and preserved in such a way that it remains evidence.
- Detailed Documentation: Document everything step by step in the forensic process because accurate documentation is very important in court.
- Track Constant Changes: The cyber-criminal changes pace with time. Updating tools and training can keep the forensic expert in advance of the threats.
- Teamwork with the Legal Expert: Be up to par with the law standards and consult with a legal expert who can work with jurisdictional issues that may arise.
- Employee Education: Educate employees on email security, phishing signs, and best practices in using the e-mail to avoid incidents from happening.
Conclusion
Email forensics has become an important area within digital forensics to gain insights into cyber incidents concerning email communication. From stopping phishing attacks to gathering admissible evidence in legal cases, email forensics is crucial to secure digital communications and retain data integrity. As email systems continue to be abused by attackers, organizations, as well as forensic experts, must remain vigilant and continuously upgrade their tools and techniques to combat evolving threats. Digi9 offers professional email forensics services, helping clients investigate email-based incidents, prevent security breaches, and ensure robust digital security.