In the evolving cybersecurity landscape, adopting Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has become essential. Zero Trust, with its “never trust, always verify” approach, significantly strengthens security, especially when integrated with Security Operations Center (SOC) collaboration. Here at Digi9, we specialize in implementing this synergy between ZTA and SOC to create resilient security frameworks that benefit organizations in today’s digital age.
1. Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
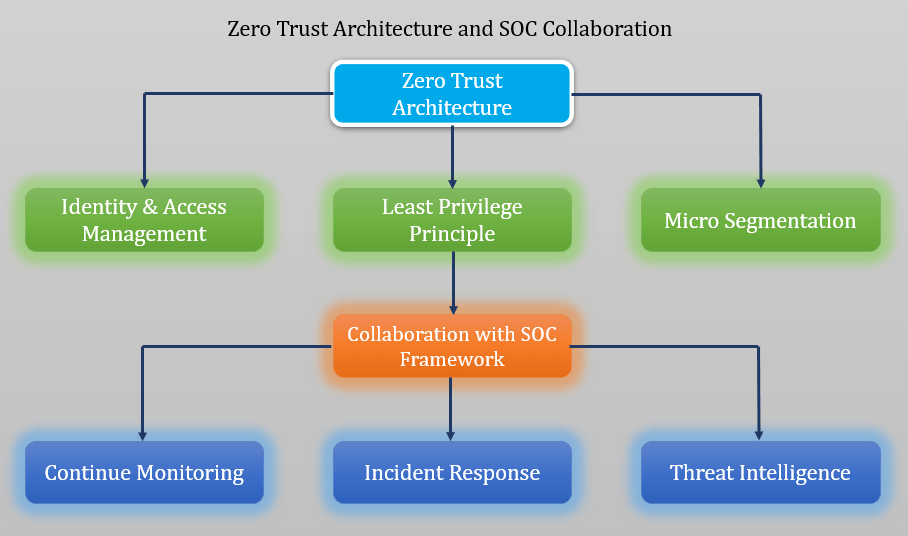
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no implicit trust within or outside an organization’s network. It mandates verification for every access request, minimizing unauthorized access and lateral movement. At Digi9, we focus on the following Zero Trust pillars:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Central to ZTA, IAM ensures that each access request is verified based on identity, time, and access policies.
- Least Privilege Principle: Zero Trust enforces minimal access rights, granting users only the necessary permissions for their tasks.
- Micro-Segmentation: Network segmentation adds granular access controls, preventing broad access even if one area is compromised.
2. SOC’s Role in Zero Trust Implementation
A Security Operations Center (SOC) detects, analyzes, and mitigates threats. At Digi9, our SOC capabilities strengthen ZTA by offering real-time monitoring, fast incident response, and detailed threat intelligence, which are crucial for effective Zero Trust. Here’s how SOC enhances Zero Trust:
- Continuous Monitoring: SOC analysts monitor network traffic, user behavior, and system vulnerabilities around the clock, identifying anomalies that could indicate threats.
- Incident Response: SOC’s quick response teams mitigate security incidents swiftly, aligning with Zero Trust’s objective of rapid threat containment.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: SOC provides intelligence on emerging threats, allowing ZTA to adapt access policies proactively.
3. Benefits of Integrating Zero Trust and SOC
Combining Zero Trust with SOC results in a fortified security posture. Digi9’s integration of ZTA and SOC brings about significant advantages, such as
- Improved Security Posture: ZTA and SOC create a strong security environment, reducing potential attack surfaces.
- Enhanced Threat Detection: Continuous SOC monitoring aids ZTA by identifying suspicious activities, preventing unauthorized access in real-time.
- Adaptability to Emerging Threats: SOC’s threat intelligence ensures that ZTA’s access policies adapt to new threat trends, offering future-proof security.
4. Implementing Zero Trust and SOC Collaboration
To maximize Zero Trust and SOC collaboration, Digi9 recommends the following steps:
- Deploy IAM and MFA to verify identities before granting access, ensuring each user is authenticated and authorized based on their role and context. This adds an essential layer of defense, preventing unauthorized users from gaining access.
- Set up network segmentation with micro-segmentation for critical assets, limiting the movement of any potential threat within the network. This approach helps isolate sensitive resources, restricting access only to necessary users and applications.
- Integrate SOC and ZTA tools to enable automated threat detection and response, allowing real-time analysis of user behavior and quick responses to unusual activity. SOC integration with ZTA tools ensures continuous monitoring, strengthening the system’s defenses.
- Conduct continuous policy reviews with SOC feedback to improve access controls as threats evolve. Regular policy updates and SOC insights help organizations stay adaptive, refining their Zero Trust approach to align with the latest threat intelligence and business needs.
Conclusion
Incorporating Zero Trust Architecture with SOC collaboration is essential for modern organizations to handle today’s cyber threats. Together, they establish a robust, adaptive, and resilient security framework capable of defending against sophisticated attacks. By embedding Zero Trust into SOC processes, Digi9 helps organizations enhance security, ensuring every access is scrutinized, every user verified, and every potential threat promptly addressed


